You only see the exquisite appearance of porcelain, but do not see the hardships behind the workers. You are amazed by the perfection of porcelain, but do not know the exquisite process. You marvel at the high price of porcelain, but cannot appreciate the sweat put in by the 72 processes of ceramic subdivision. Below, I will briefly introduce how stone and soil become exquisite ceramics.
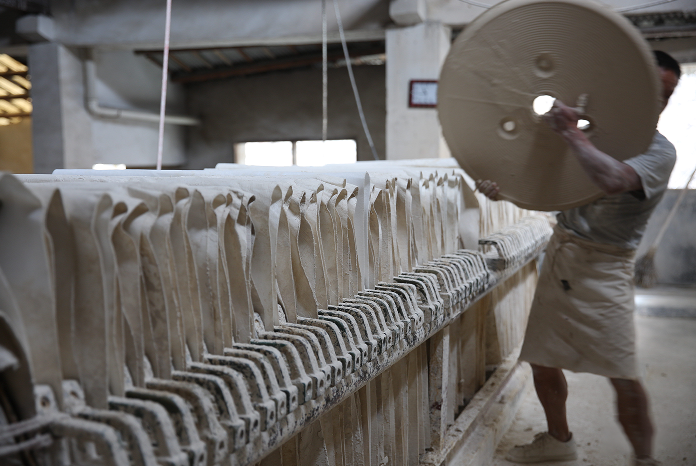
1. Refining mud
Porcelain stone, kaolin, quartz stone, mullite and other materials are the best raw materials for firing porcelain. For thousands of years, many high-quality ceramics have evolved from this inconspicuous porcelain clay. The first process of making porcelain is to refine the clay into usable porcelain clay.
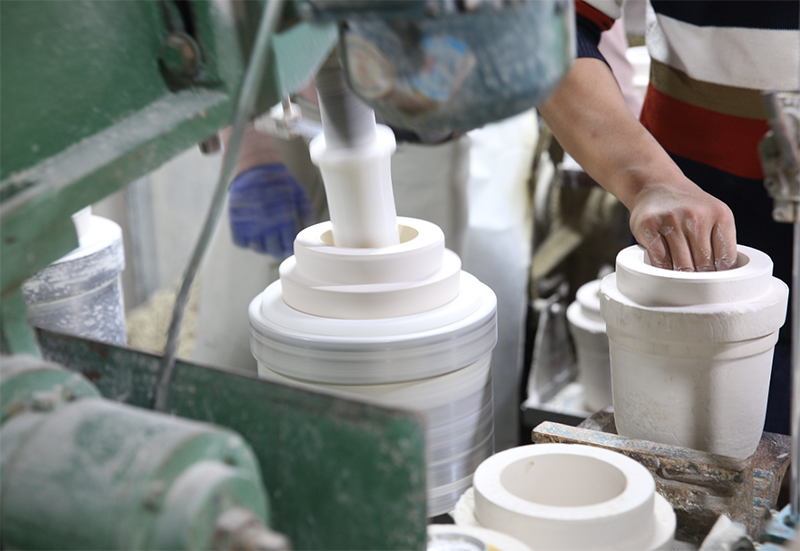
2. Forming
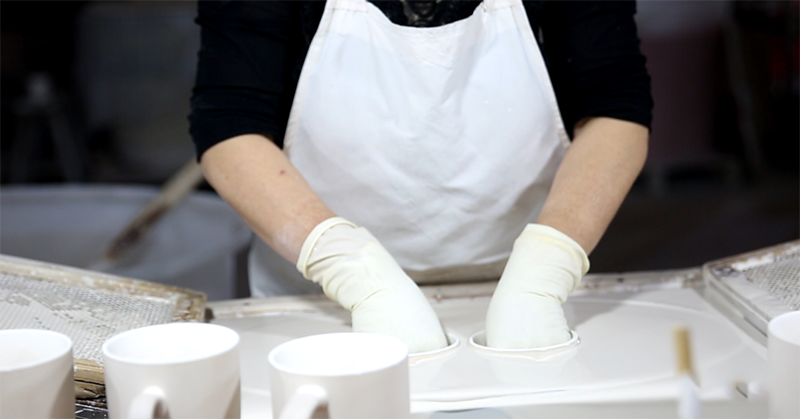
(1) Grouting molding
Grouting molding, also known as casting molding, is based on the physical properties of porous gypsum molds that can absorb moisture. Ceramic powder is mixed into a flowable slurry and then injected into porous molds (mainly gypsum molds). After the moisture is sucked into the mold (gypsum), a uniform mud layer with a certain thickness is formed. During the dehydration and drying process, a solid body with a certain strength is also formed. This method is called grouting molding.
(2) Rolling forming
Rolling forming is a new process developed from rotary forming, which improves the shape of the rotary forming blade into a rotating rolling head. When forming, use a rolling head and a model to rotate around their own axis at a certain speed and in the same direction. Due to the rotation of the rolling head, the mud material in the model is rolled and extended into a blank.
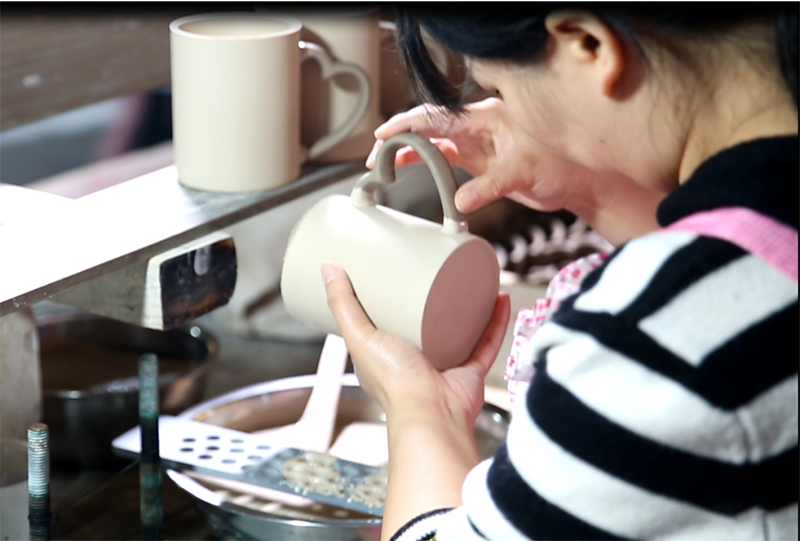
3. Handle production
Customize ceramic cups according to requirements, carve sample molds with the same shape and enlarged proportion (thermal shrinkage ratio), and make finished ceramic cup molds based on the sample molds
4. Handle connection
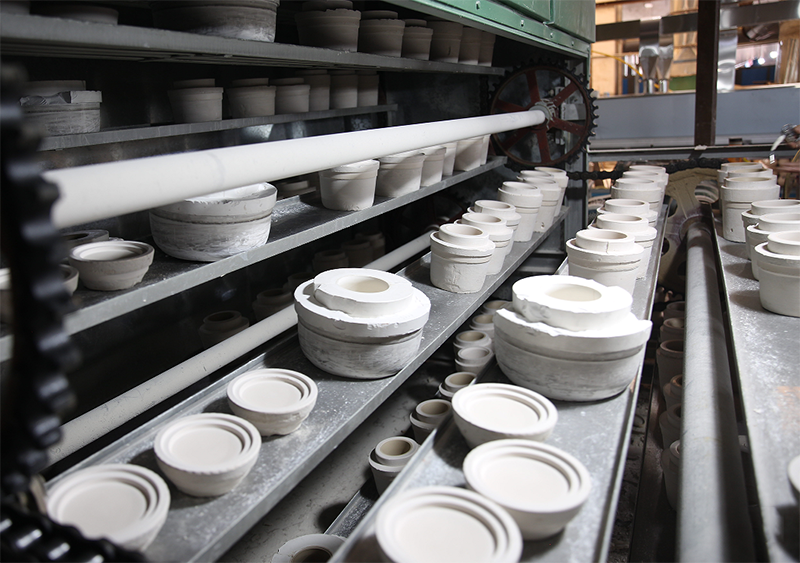
5. Embryo repair
Remove the ceramic cup from the mold, repair the excess mud on the mold line with a blade, and then clean the ceramic cup with a sponge until it is smooth and free of protruding mud spots.
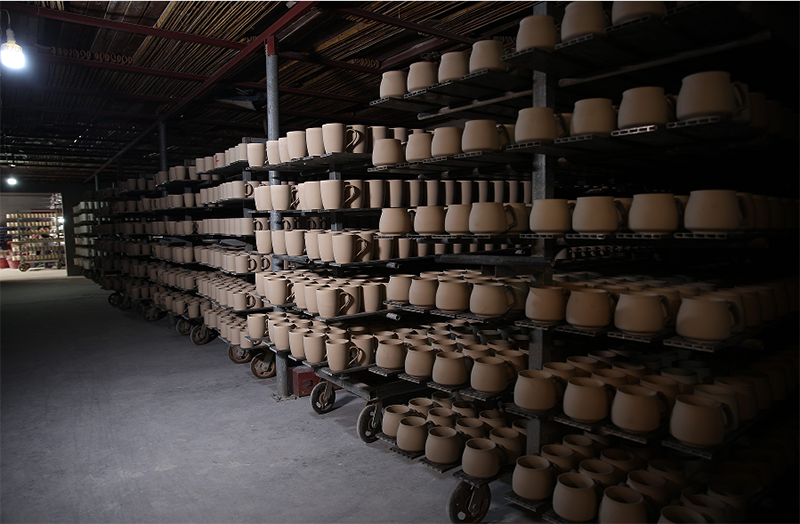
Place the ceramic cup in the drying room for baking, only the dried ceramic cup can cover the glaze surface when glazed.
7. Glazing
The finished porcelain embryo is rough and dull, and glazing is divided into outer glazing and inner glazing. Some ceramic cups are fully glazed, some are partially glazed, some are glazed at once, and some are glazed several times. After glazing, it is completely different, smooth and bright.
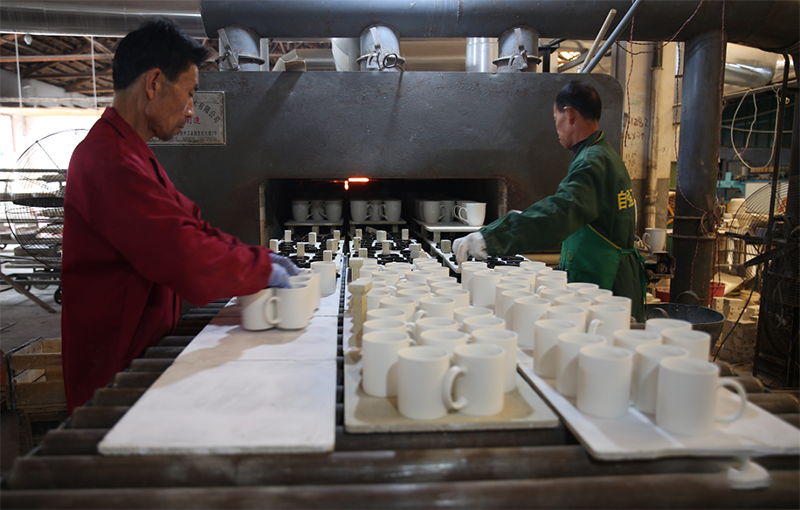
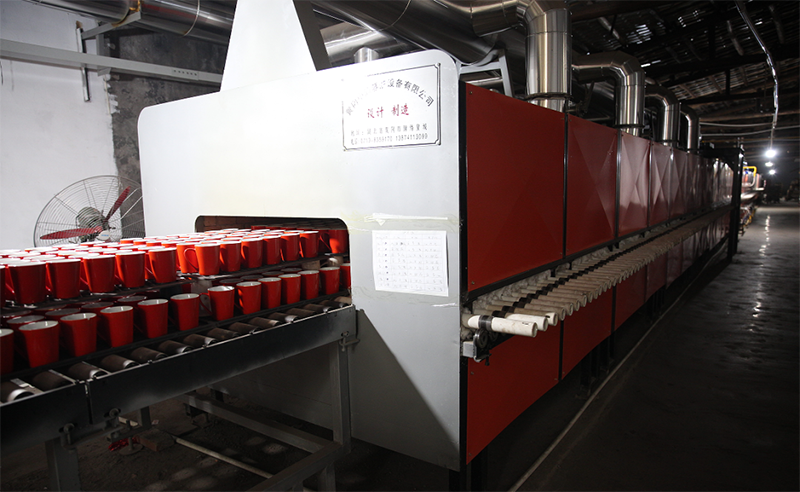
8. Kiln firing
The highest temperature for firing is generally around 1300 degrees, which is usually a cycle of high and low temperatures such as low temperature high temperature low temperature. The thousand year old kiln fire continues endlessly, and the porcelain embryo, finely carved and ground by dozens of tools, undergoes a thousand degree high temperature burning in the kiln, like an ugly duckling turning into a white swan.
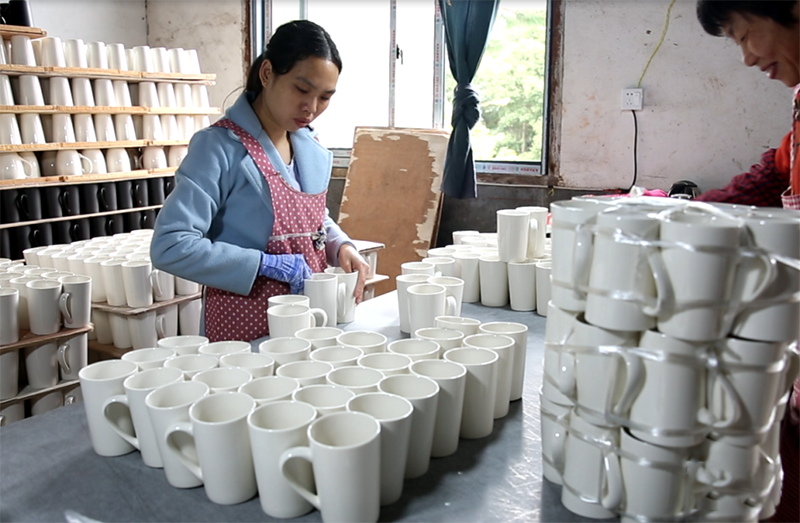
9. Quality inspection
After high-temperature refining, the porcelain blanks in the kiln have become exquisite pieces of porcelain, eagerly standing out from the open kiln door. After complete cooling, the quality inspector screens out the unqualified defective ceramic cups.
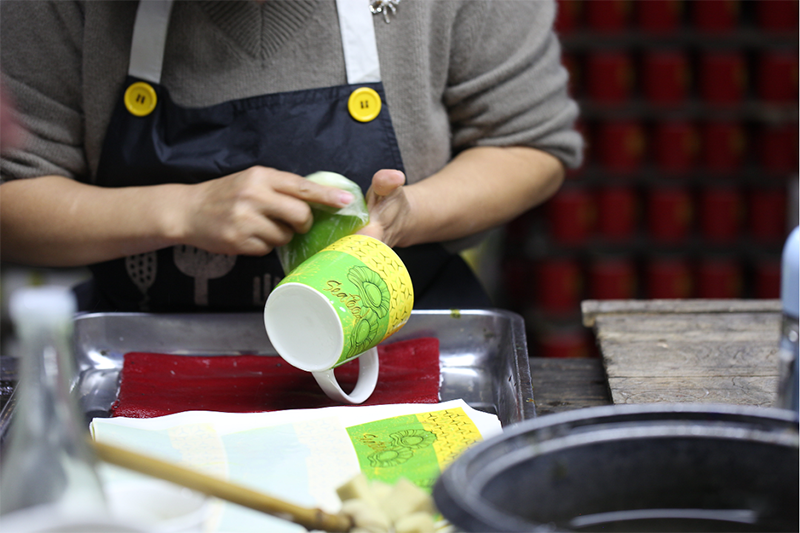
10. Stickers
If the customer requests decorative patterns, logos, etc., we will apply stickers according to the specific situation to ensure that the color of the pattern meets the requirements.
11. sticker firing
Put the cup with the flower paper pasted on it into the kiln for secondary baking. The key to baking the flower lies in the temperature, which is constrained by the color of the flower paper and the material of the ceramic cup. That is to say, different colors require different temperatures to be baked in order to make better products. The temperature of baking the flower paper should be just enough to make the glaze on the ceramic cup start to melt. At this time, the ceramic colorant on the flower paper will penetrate into the glaze. When the product cools down, the color and ceramic cup become one, thus achieving the goal of preventing the ceramic cup from fading.
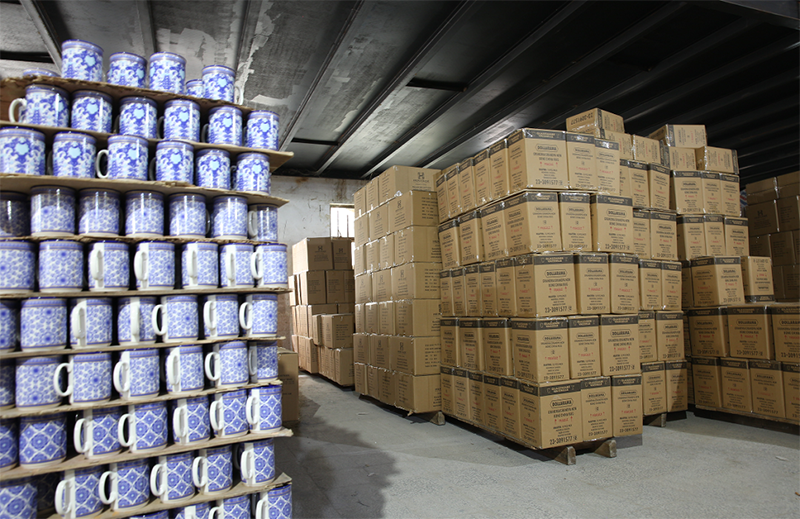
12. packaging and warehousing
After the finished product with the pattern is fired, it is inspected and packaged by quality inspectors.
Post time: Aug-29-2025